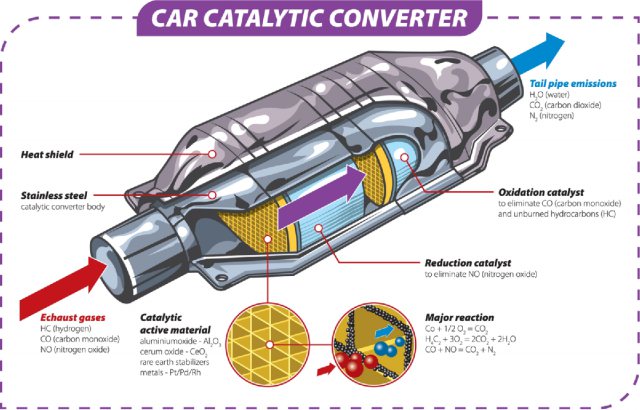
A catalytic converter is a device used in the exhaust system of internal combustion engines, such as those in cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Its primary function is to convert harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
The main pollutants targeted by catalytic converters are nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and unburned hydrocarbons. Inside the catalytic converter, a catalyst, typically composed of platinum, palladium, and rhodium, facilitates chemical reactions that transform these pollutants into less harmful compounds. For example, nitrogen oxides are converted into nitrogen and oxygen, carbon monoxide is converted into carbon dioxide, and unburned hydrocarbons are converted into carbon dioxide and water.
The catalytic converter plays a crucial role in reducing air pollution and meeting emission standards set by environmental regulations in many countries. It has become a standard component in modern vehicles, contributing to cleaner air and better environmental protection.
How catalytic converter works
The catalytic converter works through a series of chemical reactions that take place on the surfaces of a catalyst. The catalyst is typically made of a combination of platinum, palladium, and rhodium. The main reactions that occur in a catalytic converter include oxidation, reduction, and the conversion of nitrogen oxides.
Here’s a simplified explanation of the process:
- Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas produced during the combustion process.
- In the catalytic converter, platinum and palladium facilitate the oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide: 2CO+O2→2CO22CO+O2→2CO2
- Oxidation of Hydrocarbons (HC):
- Unburned hydrocarbons in the exhaust are also harmful pollutants.
- The catalyst helps oxidize these hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water: CxHy+(x+y4)O2→xCO2+y2H2OCxHy+(x+4y)O2→xCO2+2yH2O
- Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx):
- Nitrogen oxides, such as nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), are converted to nitrogen and oxygen.
- Rhodium facilitates the reduction of nitrogen oxides: 2NO+2CO→N2+2CO22NO+2CO→N2+2CO2
- Overall Reaction:
- The combined effect of these reactions results in the conversion of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen.
The catalytic converter operates efficiently at high temperatures. It relies on the heat generated during the combustion process to initiate and sustain these chemical reactions. Modern vehicles are equipped with oxygen sensors that provide feedback to the engine control system, allowing it to maintain the optimal air-fuel mixture for efficient catalytic converter operation.
Catalytic converter and impact on engine performance
While catalytic converters play a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions and meeting environmental regulations, they can have some impact on engine performance. Here are a few factors to consider:
- Backpressure:
- Catalytic converters introduce some degree of exhaust system backpressure. Backpressure occurs as exhaust gases flow through the catalytic converter, which can affect the engine’s ability to expel exhaust gases efficiently.
- High levels of backpressure may slightly reduce engine efficiency and power. However, modern catalytic converters are designed to minimize this impact, and improvements in technology have mitigated these concerns.
- Temperature Sensitivity:
- Catalytic converters require high operating temperatures to function efficiently. Cold starts and short trips may not provide the ideal conditions for the catalytic converter to reach its optimal temperature quickly.
- Some vehicles use additional systems, such as air injection or electric heaters, to raise the temperature of the exhaust gases and catalytic converter during cold starts, minimizing the impact on performance.
- Durability and Maintenance:
- Over time, catalytic converters can degrade or become clogged due to the accumulation of contaminants. This can lead to a reduction in engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Regular maintenance and addressing any issues with the catalytic converter, such as replacing a malfunctioning unit, can help maintain optimal engine performance.
- Fuel Efficiency:
- While the primary purpose of a catalytic converter is emission reduction, improvements in its design and materials have minimized the impact on fuel efficiency. In fact, efficient emission control contributes to meeting fuel efficiency standards by optimizing combustion.
It’s important to note that the impact of a catalytic converter on engine performance is generally minimal in modern vehicles. Technological advancements have allowed manufacturers to design catalytic converters that balance emission control with performance considerations. Additionally, the benefits of reduced air pollution and compliance with environmental regulations often outweigh any modest impact on engine performance.
Targeted for theft?
Catalytic converters are often targeted for theft due to the valuable metals they contain, such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These precious metals, particularly rhodium, have high market value. Thieves steal catalytic converters to sell the metals on the black market or to scrap yards that may not ask many questions about the origin of the materials.
Here are a few reasons why catalytic converters are attractive to thieves:
- Precious Metals Value:
- Catalytic converters contain small amounts of precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals, especially rhodium, can be more valuable per ounce than gold. The relatively small size of the catalytic converter makes it a concentrated source of these precious metals.
- Ease of Theft:
- Catalytic converters are typically located underneath vehicles and are relatively accessible. Thieves can use simple tools, such as a saw or a wrench, to quickly remove the catalytic converter. The theft can be completed in a matter of minutes.
- Lack of Serial Numbers:
- Unlike other car parts, catalytic converters often lack identifiable serial numbers or markings, making them difficult to trace back to a specific vehicle. This anonymity makes it easier for thieves to sell the stolen converters without detection.
- Vulnerability of Certain Vehicles:
- Some vehicles, such as trucks and SUVs, are more vulnerable to catalytic converter theft because they have higher ground clearance, making it easier for thieves to access the converters. Additionally, hybrid vehicles are often targeted because their converters contain a higher amount of precious metals.
To deter catalytic converter theft, some individuals and businesses have taken preventive measures, such as installing protective shields, welding the converters to the vehicle frame, or using specialized security devices. Additionally, law enforcement agencies and scrap yards may implement measures to track and identify stolen catalytic converters.
The prevalence of catalytic converter theft has led to increased awareness and efforts to address the issue, both through preventive measures and law enforcement initiatives.





